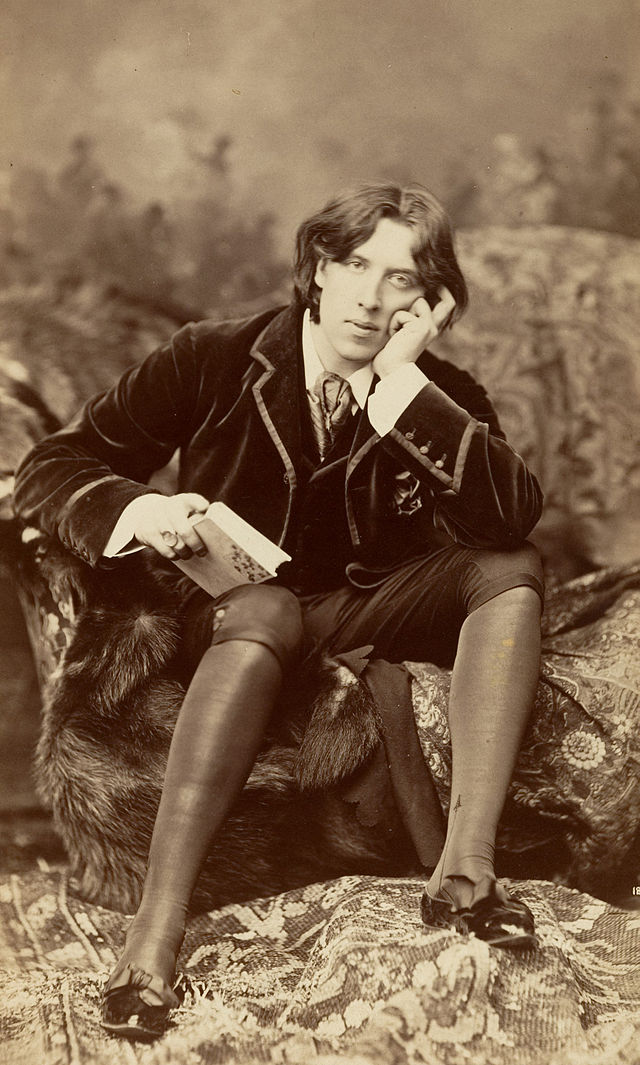
Oscar Wilde in 1882, before he was sentenced to prison for “gross indecency…”
January 30, 2015 – I just saw The Imitation Game, a “2014 historical thriller film about British mathematician, logician, cryptanalyst and pioneering computer scientist Alan Turing who was a key figure in cracking Nazi Germany‘s naval Enigma code which helped the Allies win the Second World War, only to later be criminally prosecuted for his homosexuality.”
This was after I’d gotten a lead connecting Psalm 130 to Oscar Wilde, who also got “sent to prison for ‘gross indecency,'” away back in 1895.
Note that all this occurred in another country – England – and before the year 2003. That’s when the U.S. Supreme Court issued Lawrence v. Texas, thus ending such sentences:
[T]he Court struck down the sodomy law in Texas and, by extension, invalidated sodomy laws in 13 other states, making same-sex sexual activity legal in every U.S. state and territory. The Court overturned its previous ruling on the same issue in the 1986 case Bowers v. Hardwick… The Court held that intimate consensual sexual conduct was part of the liberty protected by substantive due process under the 14th Amendment. (E.A.)
Thus as a general rule it pays to remember our past history. That’s good advice even when – and perhaps especially when – that history isn’t all that glorious. As Harry Truman once said, “The only thing new in the world is the history you don’t know.” (See Harry Truman and his History Lessons, and also my fairly-recent post On Harry Truman and the next election.)
Which brings us back to Alan Turing and Oscar Wilde.
Wikipedia said this: “The film’s closing titles tell of Turing’s suicide in 1954, the royal pardon granted to him in 2013, and how his [code-breaking] machine inspired the invention and design of modern computers.” Turing’s suicide followed – and may have been caused by – his court-ordered Chemical castration. (Turing had been given the “choice” of spending some two years in prison or taking the court-ordered drug treatment…)
Wilde on the other hand got two years of hard labor, without a choice of “castration.” And when he tried to speak, his voice was drowned out by cries of “‘Shame’ in the courtroom.”
Wilde was imprisoned first in Pentonville Prison and then Wandsworth Prison in London. Inmates followed a regimen of “hard labour, hard fare and a hard bed,” which wore very harshly on Wilde… His health declined sharply, and in November he collapsed during chapel from illness and hunger… He spent two months in the infirmary… Richard B. Haldane, the Liberal MP and reformer, visited him and had him transferred in November to Reading Prison… The transfer itself was the lowest point of his incarceration, as a crowd jeered and spat at him on the railway platform.
See Oscar Wilde – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Which brings up Psalm 130.
Between January and March 1897, near the end of his prison term, Wilde wrote a letter.
The letter was sent from “Reading Gaol to Lord Alfred Douglas.” The title of the letter was De Profundus. Psalm 130 is one of the “Penitential psalms.” In English it begins: “Out of the depths I cry to you, O Lord!” The Latin for “out of the depths” is De Profundus, and that’s where the title comes from. See De Profundis (letter) – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Which brings up the popular opinion that some of the world’s best writing has been done in prison. See for example 12 Famous Writers Who Did Time | Robert Rotstein – Huffington Post, and 10 Great Works of Literature Written in Prison – Flavorwire:
When we imagine the places where our favorite authors penned their greatest masterpieces, a jail cell usually doesn’t come to mind. But, whether their writers were prisoners of war or victims of bigotry, the solitude and lack of distractions have produced many a great book. From Oscar Wilde’s apologia on spiritual awakening to Thoreau’s thoughts on civil disobedience, we survey authors whose great mental escapes from incarceration resulted in some of their most insightful and profound works…
Whether that solitude and “lack of distraction” still applies in today’s prisons is a matter of debate. But a fairly recent example does come to mind, Martin Luther King’s Letter from Birmingham Jail – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Written on April 16, 1963, the open letter “defends the strategy of nonviolent resistance to racism, arguing that people have a moral responsibility to break unjust laws… The letter was widely published and became an important text for the American civil rights movement of the early 1960s.”
In Wilde’s case both the prologue and epilogue of his letter were a bit different.
Throughout the 1880’s Wilde had been a popular London playwright. He was noted for his epigrams – his “witty, ingenious or pointed sayings” – and a novel The Picture of Dorian Gray. Then there were the plays, including a “masterpiece,” The Importance of Being Earnest. Also:
He wrote Salome (1891) in French in Paris but it was refused a licence for England due to the absolute prohibition of Biblical subjects on the English stage. Unperturbed, Wilde produced four society comedies in the early 1890s, which made him one of the most successful playwrights of late Victorian London…
But Wilde’s world came crashing down when he filed the ill-advised lawsuit that led to his own arrest, trial and conviction for gross indecency. In brief, he went from the heights of fame and pleasure, literally to “the depths.” And there, for whatever reason, he found “serenity:”
In 1897, in prison, he wrote De Profundis, which was published in 1905, a long letter which discusses his spiritual journey through his trials, forming a dark counterpoint to his earlier philosophy of pleasure. Upon his release he left immediately for France, never to return to Ireland or Britain. There he wrote his last work, The Ballad of Reading Gaol (1898), a long poem commemorating the harsh rhythms of prison life. He died destitute in Paris at the age of 46.
In other words, he “lost everything dear to him,” but didn’t blame external forces. The letter quoted Isaiah 53:3 He was despised and rejected by mankind, and came to see “Christ as a Romantic artist.” In a word, instead of blaming other people, Wilde “rather absorb[ed] his hardships through the artistic process into a spiritual experience.” See Oscar Wilde, De Profundis, and also Voices from Solitary: Oscar Wilde’s Cry from the Depths.
Incidentally, Wilde had to publish his last work, “Reading Gaol,” under an assumed name:
The finished poem was published by Leonard Smithers in 1898 under the name C.3.3., which stood for cell block C, landing 3, cell 3. This ensured that Wilde’s name – by then notorious – did not appear on the poem’s front cover… It was a commercial success, going through seven editions in less than two years…
So, in a few short years Oscar Wilde went from the highest acclaim to cries of “shame” in the courtroom. When he was transferred to Reading Prison, a crowd gathered to jeer and spit at him. During his exile in France he had to publish his last work under an assumed name.
And now he brings tourists to Dublin, the city of his birth…
Aside from his statue in Dublin’s Merrion Square, there’s also an Oscar Wilde Centre, at Trinity College in Dublin. Which brings to mind what John Steinbeck wrote about another writer…
In his book Travels with Charley, Steinbeck wrote of wanting to see Sauk Centre, where Sinclair Lewis was born. It was also the metaphoric setting of Lewis’ satirical novel, Main Street.
As Wikipedia noted, the novel was set in Gopher Prairie, “a town modeled on Sauk Centre.” The heroine, Carol Milford, is a free-spirited liberal who disdains “the town’s physical ugliness and smug conservatism.” The novel itself portrayed “petty back-stabbers and hypocrites in a small town.” It mocked the prevalent desire to live in such “‘wholesome’ small towns,” with its “vicious realism and biting humor.” Small wonder then that some “small-town residents resented their portrayal and the book was banned in Alexandria, Minnesota.”
Small wonder too that when Steinbeck met him in his later years, Lewis was shrunken, shriveled and constantly cold. So he too took a voluntary exile – he died in Rome, of advanced alcoholism – prompted in part by the violent hatred his novel “aroused in the country of his nativity.” But now, as Steinbeck noted, “There’s a sign in Sauk Centre all right: ‘Birthplace of Sinclair Lewis:'”
The only good writer was a dead writer. Then he couldn’t surprise anyone any more, couldn’t hurt anyone any more…. I’ve heard he died alone. And now he’s good for the town. Brings in some tourists. He’s a good writer now.
There’s probably some kind of lesson there, for writers and for bloggers. In the meantime, here’s Psalm 130 – that Oscar Wilde found so comforting in his later years – in its entirety:
Out of the depths I cry to you, O Lord. Lord, hear my voice! Let your ears be attentive to the voice of my supplications! If you, O Lord, should mark iniquities, Lord, who could stand? But there is forgiveness with you, so that you may be revered. I wait for the Lord, my soul waits, and in his word I hope; my soul waits for the Lord, more than those who watch for the morning, more than those who watch for the morning. O Israel, hope in the Lord! For with the Lord there is steadfast love, and with him is great power to redeem. It is he who will redeem Israel from all its iniquities.

The upper image is courtesy of Oscar Wilde – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, with the caption: “Photograph taken in 1882 by Napoleon Sarony.” The lower image comes from the same article, with the caption: “Statue of Oscar Wilde in Merrion Square, Dublin:”
[Merrion Square] is a Georgian garden square on the southside of Dublin [and is] considered one of the city’s finest surviving squares. Three sides are lined with Georgian redbrick townhouses; the West side abuts the grounds of Leinster House (seat of the Oireachtas),Government Buildings, the Natural History Museum and the National Gallery. The central railed-off garden is now a public park.
The full reference to the movie-lead reference is Imitation Game – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. The full reference to the Lawrence case is Lawrence v. Texas – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. The full reference to Turing’s “rehabilitation” is Chemical castration – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Re: Steinbeck on Sinclair Lewis. See Travels with Charley, Penguin Books (1980), pages 133-34. See also Sinclair Lewis Biography – CliffsNotes: “Although the reaction of Sauk Centre toward the book was at first unfavorable, there is no evidence that it was ever banned from the local library.” And see Main Street (novel) – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Psalm 130 was quoted in the New Revised Standard Version (NRSV).